The 22nd seminar
“What is the toilet comfort ?” -1
– “Evolving Toilets” book series, volume 1 “Comfortable Toilets” edited by Japan Toilet Association
Japan Toilet Association (JTA) Seminar Series; “Let us know more about our Toilet Story”
Date: 16 March 2023 (Thu) 18:00-20:00 JST
Moderator: Junko Kobayashi, Ph.D. (JTA chairperson, CEO of Gondola Design Office/ architecture)
Presenters:
(1)What is meant by “Comfort”, Yoshinori Komatsu, Ph.D. (JTA steering committee member, Nagoya Institute of Technology Faculty of Engineering, Department of Social Engineering, in the field of architectural design)
(2)History and culture of comfortable toilets, Mr. Hideki Morita (JTA steering committee member, Toilet researcher/ toilet history)
(3)Toilet ergonomics, Yoshiyuki Ueno, Ph.D. (JTA deputy chairperson, former professor of Chiba Institute of Technology)
Organizer:
Yoshihiko Kawauchi, Ph.D., JTA steering committee member, Former professor of Toyo University.
(Kobayashi) We have been making continuous improvements in pursuit of the comfortable environment for the toilet. Everyone has different senses of the comfort in practice. The second volume titled “Comfortable Toilet” in the “Evolving Toilet” series books edited by the Japan Toilet Association. The authors firstly thought about the meaning of the toilet comfort, then learned about the history, and understood the evolution of the technology, finally considered what kind of problems are existing today? 37 specialists from each field gathered and compiled them as co-authors. Associate Prof. & Dr. Komatsu will talk first about what is meant by “Comfort.” Then Mr. Morita will talk about the history of the toilet comfort, and former professor and Dr. Ueno will lastly talk about the ergonomics including the comfort.
(1)What is meant by “Comfort”: Associate Prof. & Dr. Komatsu
The comfort in the building
(1-1)The toilet is subject to various architectural restrictions since it is a part of the building. We must think about the comfort within those constraints. There are several evaluation axes to measure the basic performance of a building. We have built the buildings in pursuit of safety and sanitation. We have repeatedly improved to make our better life to reside with more comfortable after fulfilling these two factors. In recent years, many buildings have been built in pursuit of convenience, economic efficiency, and sociality in cities. A new feature called sustainability has come into demand recently. These trends will also apply to the toilets spontaneously.
The comfort is difficult to define. I would like to divide it into three levels.
(1-2) Level1: A toilet satisfies the basics
The first and low level is a toilet satisfies the basic matters such as not insecure, not unsanitary, not inconvenient. In other words, the Level 1 toilet can be defined as non-discomfort. I think that toilets with this kind of passive comfort will be a common factor for many people when thinking about the comfortable toilets. It can be said that a toilet comfort is a state where is without or a little stress.
(1-3) Level 2: Satisfactory comfort
The second level of comfort will be a state of mind that can be satisfactory for the thermal environment. The level 2 of satisfactory comfort is a sense of the temperature and the resulting mental satisfaction, which can be distinguished from the level 1 of the comfort without uncomfortable. However, both first and second levels comforts tend to be passive. These comforts can be classified that have little individual differences, or comforts that do not reflect individual differences.
(1-4) Level 3: Stimulus Comfort
For instance, when we look directly at the headlights of an oncoming car, we feel dazzled and uncomfortable, or we cannot see the surroundings. However, we don’t feel uncomfortable with the naked light bulbs at the festival market. Even if it is dazzling, we can feel the brilliance and liveliness. In other words, whether it is unpleasant or comfortable will change depending on how you perceive it even with the similar feature of the light. For this reason, the third level of comfort can be as the comfort of being stimulated. The consonance music tune gives comfort to many people, but some people find pleasure and pleasantness in dissonance music tune. While comfort is common to many of us who have few objections, pleasantness can be said to be a third level of comfort that varies extremely from person to person. Thus, there are three levels of comfort: non-discomfort, satisfactory, and stimulus.
(1-5) Will the comfort continue?
The sensory comfort of the level 1 which is not discomfort is common to all people, and it will endure being comfortable relatively stable. The level 2 comfort due to the satisfaction of the state of mind and the level 3 comfort will be stimulated fluctuate greatly depending on changes in the state and the environment. The comfort is felt not only the passage of time but also the influence of their surroundings. In other words, it is not always possible to be felt comfortable all the time.
(1-6) Is it admittable to seek endless comfort?
The economic efficiency and sustainability in buildings are factors that constrain the comfort. We can pursue various comforts and create the most comfortable toilet with ignoring the cost. The clean water we use every day uses a lot of energy from a sustainability point of view. In addition, the washed sewage is problematic from a sustainability constraint as it uses a lot of energy during purification. In addition, there may be a risk that the pursuit of only momentary comfort may compromise health and safety. Even if it is comfortable for an instant, it cannot be said “It is comfortable”, if it damages the human health consequently and lasts for a long time.
(1-7) Summary
I have to say the toilet comfort is not always stable or universally acceptable. The toilets keep our safety and health, and furthermore they are not uncomfortable and we feel comfortable in our state of mind. Sometimes it would be nice to have a toilet which gives creative stimulation and pleasantness.
(2) The history and culture of comfortable toilets: Mr. Hideki Morita
(2-1) The comfort with the safety at the primitive age
How did we excrete with evolving? They must defecate quite generously. However, humans were very weak creatures that did not have fangs, poison, or shells to protect themselves. We can guess the excretion of primitive age was a matter of life or death. Therefore, it is considered that keep safety during the excretion was quite serious matter.
(2-2) The comfort by separating the toilet location (B.C., prehistoric Jomon era)
There are many parasite spawns were found in the small valley at the Sannai-Maruyama site, an early Jomon era site in Aomori Prefecture in northern Japan. This valley is presumed to be a place where all excrements were dumped. There must be some sort of drainage system that would carry the excrements to accumulate in the valley or they might have been carried there and dumped. This valley is a bit remote from the village, and I presume that they kept the distance from their living places and throw away their feces and urines to ensure comfort.
Similarly, there is the Torihama shell mound at Lake Mikata, which faces Wakasa Bay in Fukui Prefecture in the middle of Japan, as an archaeological site of the Jomon era. There found the traces of stakes on the beach at this Torihama Shell Midden and many fecal fossils were found. It is presumed that a pier-shaped building was built and used it as an old age toilet. I cannot imagine whether they defecated there or threw them from the pier. However, it can be said that they were thrown away remote from the village. In this way, we can speculate that the Jomon people’s attitude of mind for the comfort was to dispose of the excrement separately and gather in one place from their daily life.
(2-3) The comfort of being washed away (8th century, Nara era in Japan)
Japan is a country blessed with quite a lot of water fortunately. There is a proverb that problems can be washed away by the water. This concept is easier to understand by the Japanese people than the foreigners. In fact, there is various naming in toilets in Japan. One name of toilet “Kawaya” means the river hut may come from the fact that the toilet was built over the river. I think that washing away with the water was one of the easy-to-understand comforts in Japan.
(2-4) The comfort that prevents dirt (from 9th to 12th centuries, Heian era in Japan)
There is an old picture scroll about a devil rewarding good fortune or punishing called “Gaki Zoshi” drawn in Heian era. There are pictures of ordinal people wearing the high clogs (Fig.1) when they use the toilet. The ground was full of feces, so it seems that they used it to prevent their feet from getting dirty. I don’t know if these the high clogs were prepared as a public property and people used them to defecate, or if they brought their own clogs to defecate. At that time, most people wore Japanese style sandals or bare feet, and high clogs must be presumably quite expensive. They are slippers nowadays, but a little while ago, there were prepared clogs in the toilet. I think it is a Japanese sensibility by wearing a kind of footwears at the toilet in order to prevent getting dirty on their feet.
It is told that the aristocrats of the old-time used potties. There was no specific space or facility called a toilet in aristocratic buildings, and instead they used a potty. It is thought that the potty was very convenient for them at the old-time to excrete without soiling their clothes. It is thought that the comfort of the toilet meant to prevent dirt at that age.
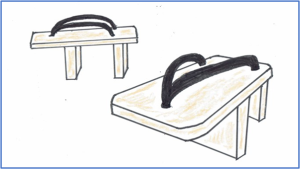
Fig.1 The high clogs
(2-5) The recycling comfort (from 12th to 19th century, Kamakura era to Edo era in Japan)
The recycling of the excrements became a fertilizer from around the Kamakura era (from 12th to 14th centuries). It can be said this was a very epoch-making event with an extreme significance in Japanese toilets history. This led to rapid standardization of the Japanese toilets. Until then, there were various types of toilets, such as defecating on the street, using a potty, or flushing. The number of toilets to collect the excrements instead of throwing it away were rapidly increasing in the nationwide. A recycling system was established to collect the excrements and use it as fertilizer. In addition, the space of the toilet has also been improved to pursue the overall comfort of the toilet.
(2-6) Modern sanitary comfort (after the latter19th century, Meiji era in Japan)
The population was concentrated in Tokyo, once called Edo era from 17th to 19th century named Edo era with more than 1 million inhabitants. However, the population in Tokyo decreased sharply as various feudal lords returned to their countryside as the Edo era ended. The population in Tokyo has halved from 1.2 million to 580 thousand. The amount of the excrements as the fertilizer that had been transported from the urban to the rural areas was halved eventually. The collecting and transporting workers also lost their jobs. The recycling system of the excrements gradually began to emaciate at the beginning of the Meiji era. On the other hand, the European scientific and modern concept of the hygiene were emerged from the 19th century onwards and were imported to Japan. A new problem arose to solve the public health problems soon after the Edo era ended and the Meiji government started as a modern society. Specifically, the countermeasures against the parasites and prevention of cholera epidemics became major issues for the Meiji government.
The Meiji government enacted ordinances in 1872 in order to keep Tokyo clean, banning the standing urination and stipulating that the excrements should be carried with a lid on the bucket. The cholera epidemic began in Tokyo from 1877. The Meiji government thought quite seriously about the sanitation, and various efforts were made to create toilets following to the modern sanitary ideas. The improved toilets were started to be built in addition to the extension of the sewers. The improved toilet had basically divided into three toilet tanks under the ground in order to prevent from the parasites. The parasite spawns will be hiding in the stool. They may stick to vegetables by the fertilizer and people will eat it. It was necessary to stop the parasites from the vicious circle.
The parasite spawns will die about three months. The toilets up to the Edo era were mixing the new feces and a month ago ones and put in a single tank and collected. This improved toilet accumulated the fresh excrement in the first tank, overflowed and moved it to the second tank, and then moved to the final tank. More than three months must have passed by the time it reaches the final tank. There will be no parasite alive when scoop up at the final tank. In addition, the spread of the sewerage will contribute the comfort with good hygiene.
(2-7) There were difference in each era about the toilet comfort.
We have once sought a comfortable toilet that is safe and comfortable. Then the comfort by separating and gathering the toilet in one place from the daily life area. The comfort of washing away. The comfort that prevents stains. The comfort in recycling.
The public toilets had a very bad reputation when the Japan Toilet Association started their activities about 40 years ago. The serious issue was how to improve the toilet and make it more comfortable. The issue was to be safe. Then ease stains by keeping the toilet cubicle and toilet bowl bright and clean. Furthermore, the filth is flushed into the sewage system, separated from the excretion site, collected in the sewage treatment plant or the septic tank, and treated in accordance with the modern hygiene concept. The sludge generated from it is recycled as the building materials. This challenge is one of the comfortable toilets that we have been working on for nearly half a century.
(3) The Toilet Ergonomics: Yoshiyuki Ueno
(3-1) How to perceive the “people, objects, and space” of the toilet
I believe that the ergonomics is a science to create things and spaces or consider to use things in the spaces. The space of the toilet must be basically centering on people.
(3-2) What kind of the toilet is suitable for the particular people ?
There are products for the dominant people and the exclusive products limited to the specific people. The urinals and crouching-type toilets are for general use and may not be suitable for some users. There is a concept in Japan named “Kyoyohin” which is a design that can be used by both the dominant people and the specific people. The sitting-style toilets must have the connotation of Kyoyohin because they can be used by more people.
(3-3) The types of the toilet bowl
The toilets are classified into the crouching-style toilet and the sitting-style toilet depending on the posture when using the toilet. There are three types of toilet bowls that we generally use: urinal, crouching-style, and sitting-style.
(3-4) Let us start by examining literature
There are few specialized books on the toilet ergonomics unfortunately. A well-known book is “The Bath Room” by Alexander Kira, which describes the ergonomics for the bath room. Furthermore, there is a description in the book “Architecture/ Interior/ Ergonomics” about toilet bowls from the field of architecture. However, there were few academic materials on toilets unfortunately.
(3-5) The mechanism of the urination
It is first necessary to know the excretion mechanism in order to examine the toilet bowl. It is especially necessary to recognize the structure of the urinary tract that emits urine. There is a difference in urination time since males have a longer urethra than females. The male urine is discharged in 90-degree twist as it spreads from the urethral meatus. This is told due to the dynamics of the liquid surface tension. The way urine is discharged and the noise of urine is different since the structures of their urethra are different in male and female. Then I drew a curve of voided urine based on the experiments.
(3-6) Measurement of the shape and dimensions of the toilet seat
The opening crotch angle is different when male and female are seated on the toilet seat of a sitting-type toilet. I sometimes wonder whether the toilet seats of today are designed for male or female. It must be better to create the different toilet seat for them, but there exists only one type.
(3-7) The sitting on the toilet bowl
The height of the sitting toilet is the most important factor for the proper posture. The common toilet seat height is almost 40 cm. Then, I modified the height and did an experiment. For example, it was about 30 cm to maintain a sitting posture and reduce the body load. The defecation requires a lot of force on the abdomen. It is commonly known that a height of about 30 cm is relatively stressless. It was found that the muscle stress increased most at the height of 40 cm when the height of the seat was changed and examined the state of muscle stress of each posture.
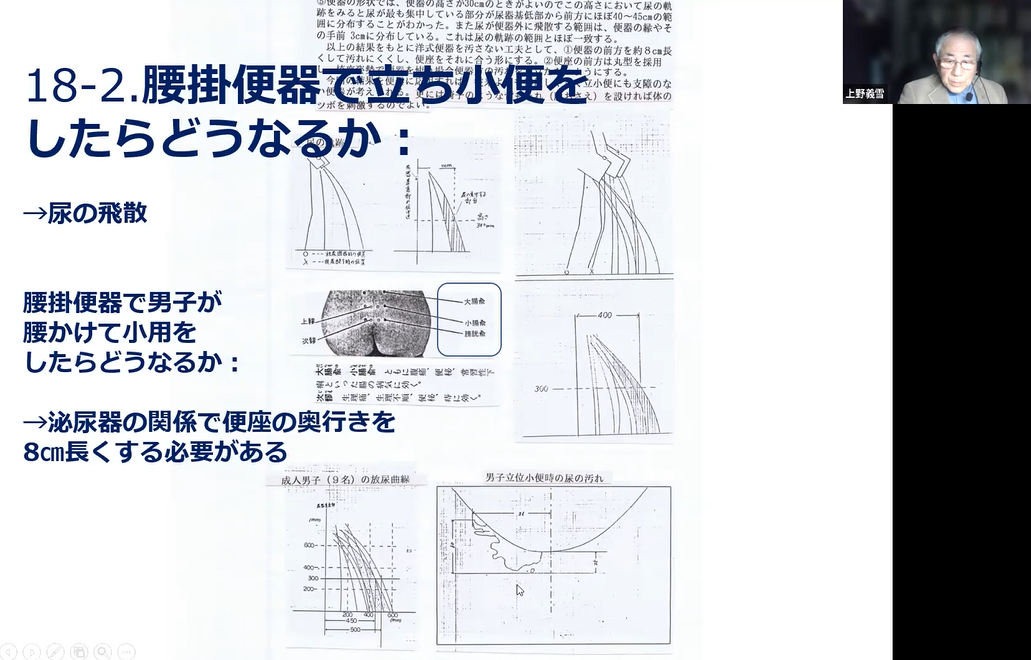
Therefore, 40 cm height is the most difficult to maintain posture. However, a backrest if there decreases the muscle stress even with 40cm. We found that the muscle stress was lowest at 30 cm in height by examining the muscle stress depending on the height of the toilet seat and the sitting time. We investigated what would be happen if a man stood up and urinated in the sitting toilet. The urine splattered on the floor in front of the toilet bowl. The situation of urine scattering changes depending on the height of the toilet bowl. 30cm height toilet brings more splash than 40 cm height ones. The front part of the trousers was also quite scattered. If a man sits on the toilet seat to urinate, the current toilet is too less spacy in the front part. The toilet must be consequently about 8 cm longer to the forward from the current one when a man sits on the toilet seat and urinates, otherwise some problem will occur.
(3-8) Crouching-style toilet
The crouching-style toilets are becoming rare in Japan these days. The surrounding of the crouching-style toilet is often wet. This was not the urine but the flushing water. A lot of water is scattered around when washing water is poured. People defecate on the surface of the bowl of the crouching-style toilet where is the shallow water to flush the excrement. A lot of water was splashing around when putting a simulated stool on it and poured out the washing water through the test experience.
(3-9) Sitting-style or crouching-style toilet?
We investigated whether the sitting-style or the crouching-style toilet is more suitable for the defecation. A blood pressure test showed which one is easier to force to the abdomen. The crouching-style was easier to push the force with a maximum of 211mmHg. On the other hand, the sitting-style is difficult to push force, and it was 186mmHg. It was found that the crouching-style is easier to induce the natural defecation. Also, when urinating, the pubic anal muscle is pulled in the sitting-style, and inhibits excretion. As a result, some urine is left over for the male case.
Whereas, the crouching-style was found that the left urine is less likely to occur. There are advantages and disadvantages to each of the crouching-style and the sitting-style where there are own histories. The number of crouching-style toilets are decreasing in recent years, but this time it will be necessary to re-consider about eliminating crouching-style toilets from the public toilets.
Q&A
(Q1: SI) If there is only a crouching-style toilet, do men squat down to urinate?
(A1: Ueno) In my case, I will squat down to urinate. Otherwise, without squat down, we can’t urinate well in the toilet bowl with a lot of splashes.
(Q2: HO) I’ve heard that koalas eat their mother’s poop. High heels were invented for walking the filth-filled streets in London.
(A2: Morita)
I’ve read that there are quite a few animals that eat the faeces of their parents. It is said that mothers inherit immunity from their parents by drinking the breast milk, but there may be a medical reason for eating their parents’ faeces. It is common for animals to eat the faeces of other animals. It is common for dogs or pigs will eat human faeces or other animals.
Talking about the origins of the high heels, European people used the potty and throw their excrement from the window to the streets which were littered with faeces. It is said that high heels were invented to avoid it. However, I think they were more like Japanese clogs rather than the high fashionable ones of today.
(C3: Kobayashi)
The school teachers still believe that pupil must change slippers at the school toilet. When renovating the toilet, it is difficult to persuade to alter their believes. The teachers are worrying that the toilet floor is dirty and the dirt will be carried from the hallway to the classroom. The recent school toilets do not wash the floor with the water when cleaning. It is kept dry and far more hygienic than in the past. Also, changing into slippers at the toilet means that the pupils still biasing that the toilet is dirty place. We, toilet designers do our best to get rid of that way of the biased thinking, but it’s hard to persuade the people to understand it.
(Q4: HO)
Recently it is called User Experience (UX) in the ergonomics. It would be normal comfort to bring it from minus to zero, but UX aims for even more comfort. When talking about the comfort in the toilet, I interpret it to mean, for example, the arranging flowers in the toilet space or the indirect soft lighting. How would Dr. Ueno think to apply UX in the modern toilet?
(A4: Ueno) I think it’s difficult for me to answer immediately at this point. Let me consider about it later.
(Q5: MU) I would like to ask something related to the noise environment of the toilet with the embarrassment. When did the Japanese people start to hide their excretion activity? Some animals will hide it from the safety to defecate. For example, I think that the toilets in Edo era (17th to 19th centuries) had short doors which were open at the top and could be seen well by the people outside at standing. I think there was an atmosphere of being less embarrassed to be seen at the ancient time because the toilet doors were small ones.
(A5: Morita) Most of the toilet doors had only the lower half during 17th -19th centuries in Edo (Now, Tokyo), but the whole part was covered in Kyoto and Osaka which was like the style of today. Even in the Edo era, I think people didn’t want to be seen by somebody or maybe they did not show it openly. There was a picture of a man peeking at a woman’s excretion an erotic book published in Edo era, and I think the reason why people liked such pictures was because they didn’t usually have the chance to see.
(Q6: MU) In the Edo era, there was a “Sound-cancelling Pot” which camouflages the excretion noise.
Did the idea of muting sound come out around the Edo era?
(A6: Morita) I’m not very familiar with this matter, but I doubt about whether the sound-cancelling pot was effective of eliminating the noise of the excrement. Furthermore, the sound-cancelling pot is placed next to the washbasin where it is out of the toilet to wash hands at the part of the hand-washing area.
(C6: MU) Today, there are devices that hide the defecation noise with the sound of running water or music. Furthermore, there are increasing number of toilets that automatically start the sound just sitting on the toilet bowl. The strong stimulus makes children with hyperacusis to cover their ears because the sound starts unexpectedly. Many people with developmental disabilities have this hyperacusis.
(Q7: Kawauchi) The current method is to overwrap with another sound. We discussed this matter at another meeting that there is also a technology of eliminating the sound by slightly shifting the frequency, like a noise canceller for the earphones.
(C8: MI) Animals that eat indigestible food such as koalas or ptarmigans, feed their offspring with the faeces of their parents, and pass on the bacteria in the intestines of their parents to their offspring to digest foods.